Converts numbers and strings to different formats.
Accepts a string format and arguments as input and returns a formatted string value based on these input.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=printf(format, arguments)")
format: A character string that comprises one or more format conversion specifiers. It must always be within single quotes (‘ ‘).
arguments: Includes one or more string, number or field name.
Example:
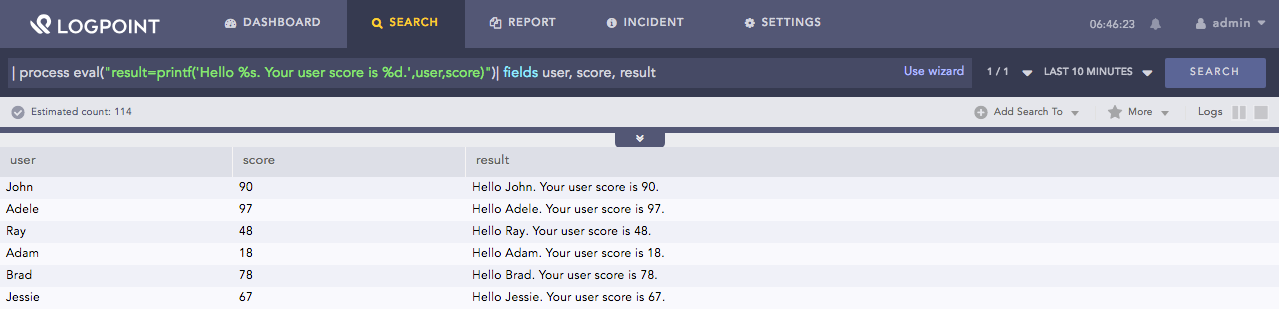
| process eval("result=printf('Hello %s. Your user score is %d.',user,score)")
| fields user, score, result
Using printf function¶
Here, the query assigns the value of the user field to %s and score field to %d and returns the defined sequence of strings in the result identifier.
The fields command displays the value of the user, score and result in a tabular form.
Accepts a string value X and a BASE as input. It converts the string X to a number by the specified BASE.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=tonumber(X, BASE)")
X can be a field name or a string value.
The BASE defines the base number to convert the string value X. It can range from 2 to 36.
Example:
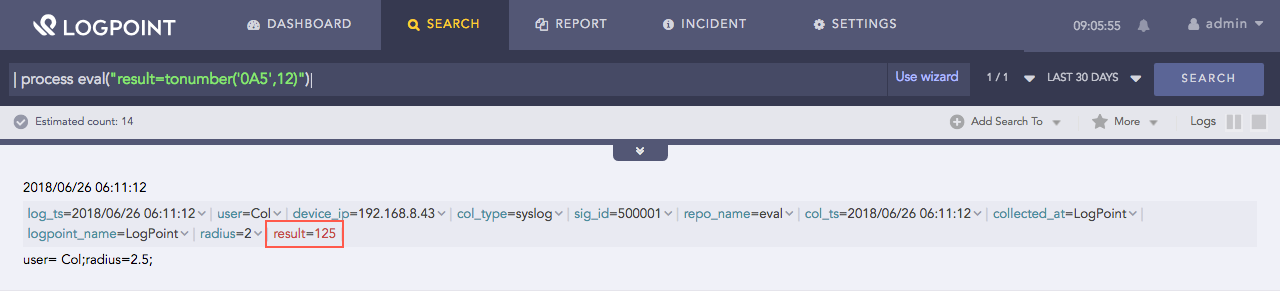
| process eval("result=tonumber('0A5',12)")
Using tonumber function¶
Here, the query converts the string value 0A5 to a number by taking base 12 and returns it in the result identifier.
Accepts an argument Y of string, long or double type as input and converts the value of Y to integer and assigns the converted value to X field.
Syntax:
| process eval("X=toint(Y)")
Example:
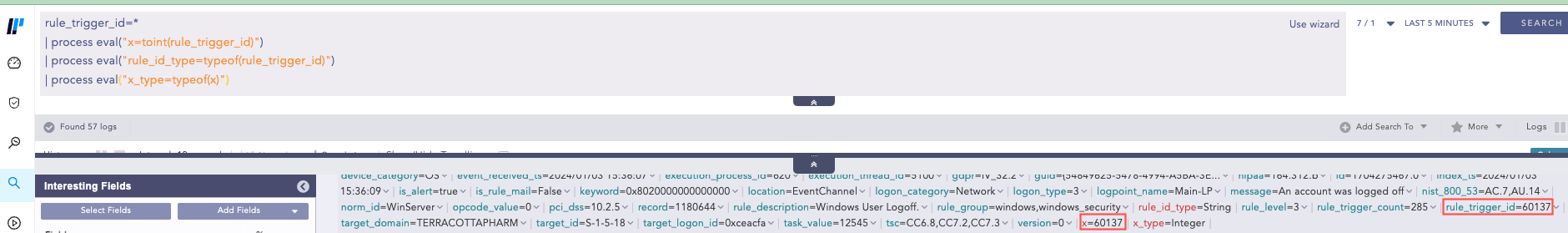
| process eval("x=toint(rule_trigger_id)")
Using toint function¶
Here, the query converts the value of rule_trigger_id to integer and assigns the value to x field.
Accepts an argument X of string or long type as input and converts the value of X to double and assigns the converted value to Y field.
Syntax:
| process eval("Y=toreal(X)")
Example:
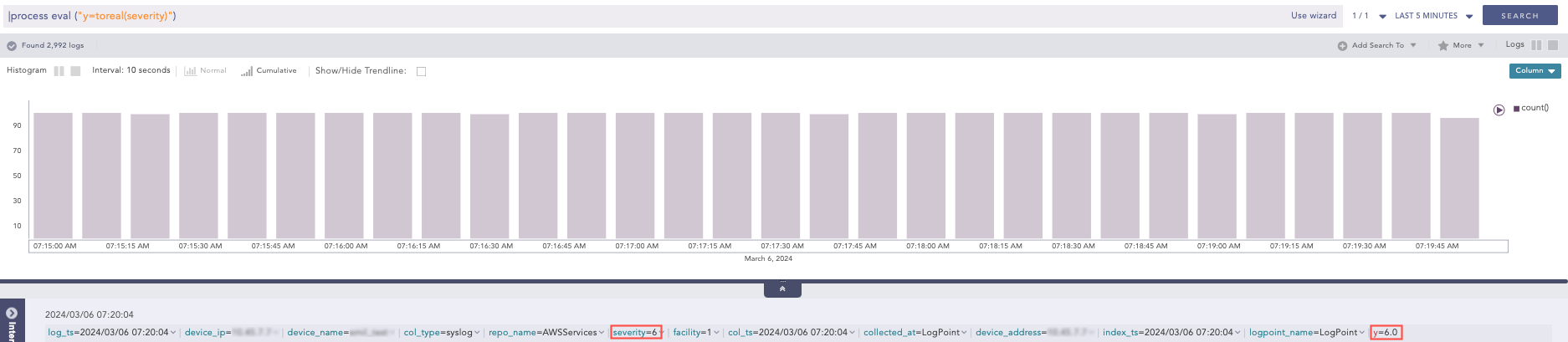
| process eval("y=toreal(severity)")
Using toreal function¶
Here, the query converts the value of severity to double type and assigns the value in y.
Accepts at least one argument X as input and converts the input value X to a string. If X is a number, the second field Y can be “hex,” “commas,” or “duration.” Y is optional.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=tostring(X, Y)")
If X is a number, the function converts the number to a string,
If X is a Boolean value, it returns the corresponding string value, True or False.
Syntax |
Description |
|---|---|
tostring(X, “hex”) |
Converts the input value X to hexadecimal. |
tostring(X, “commas”) |
Formats the input value X with commas. If the number includes decimals, it is rounded to the nearest two decimal places. |
tostring(X, “duration”) |
Converts the input value X (in seconds) to the readable time format HH:MM:SS. |
Example 1:
| process eval("x=tostring(12)")
Here, the query converts the numeric value of 12 to string.
Example 2:
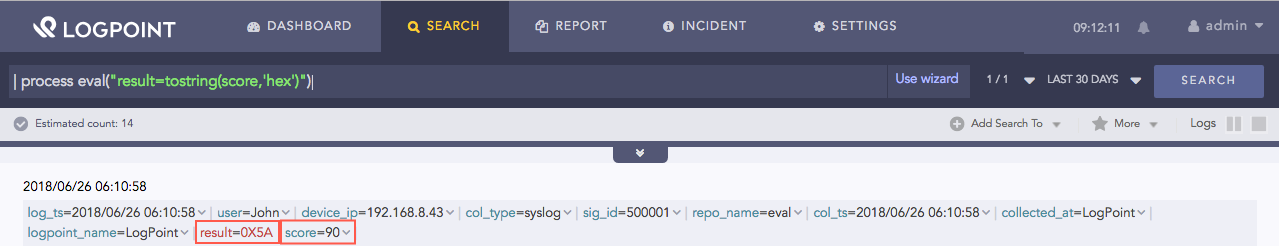
| process eval("result=tostring(score,'hex')")
Using tostring function¶
Here, the query converts the numeric value of the score field to its corresponding hexadecimal string value and assigns it in the result identifier.
Example 3:
| process eval("x=tostring(65,'duration')")
Here, the query converts the numeric value 65 into the readable time format HH:MM: and returns it in the x identifier.
Example 4:
| process eval("x=tostring(65132.6789,'commas')")
Here, the query formats the numeric value 65132.6789 with a comma and rounds the decimal value to the two decimal place (hundredths position) and returns it in the x identifier.
We are glad this guide helped.
Please don't include any personal information in your comment
Contact Support